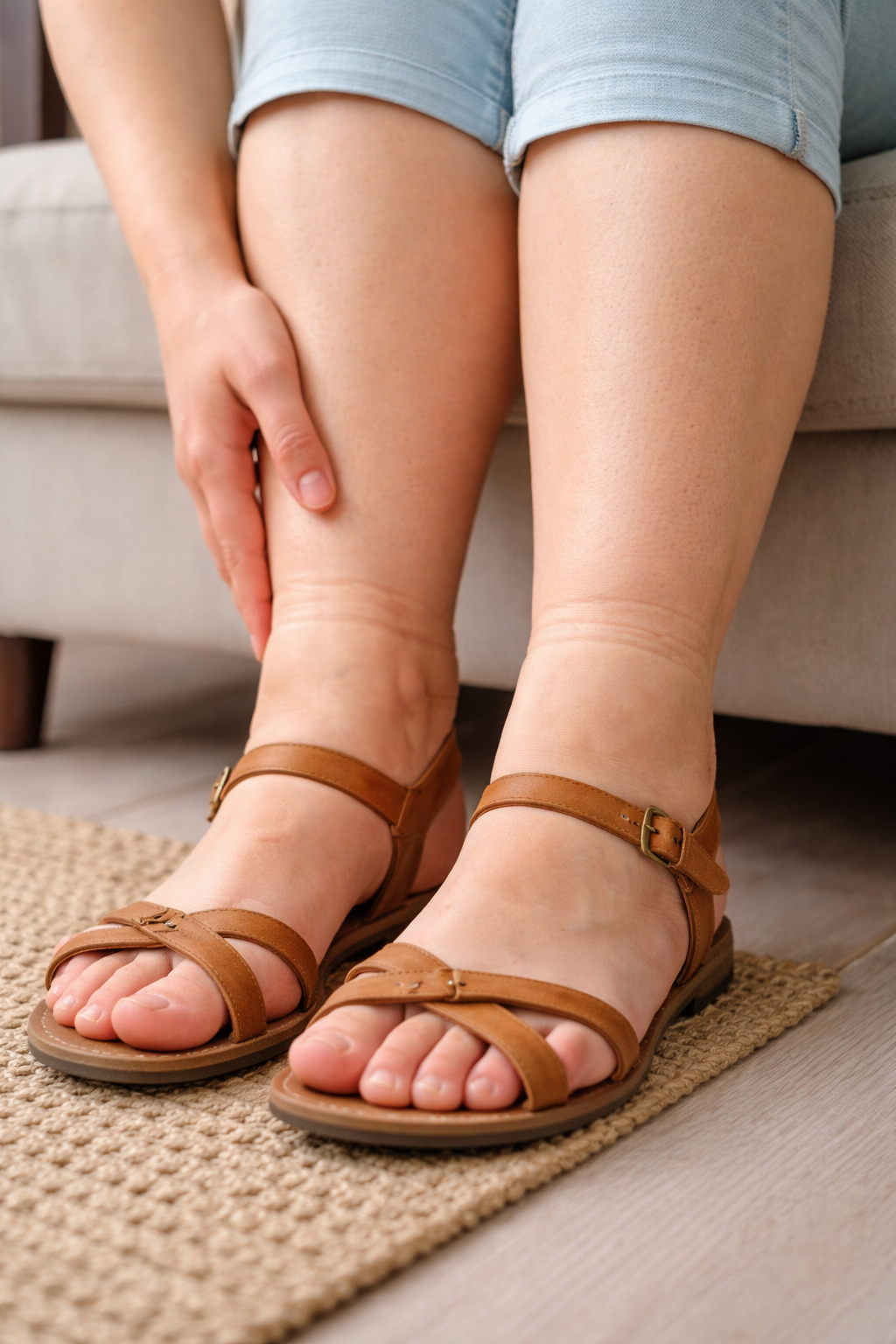
See why swelling is so common in women
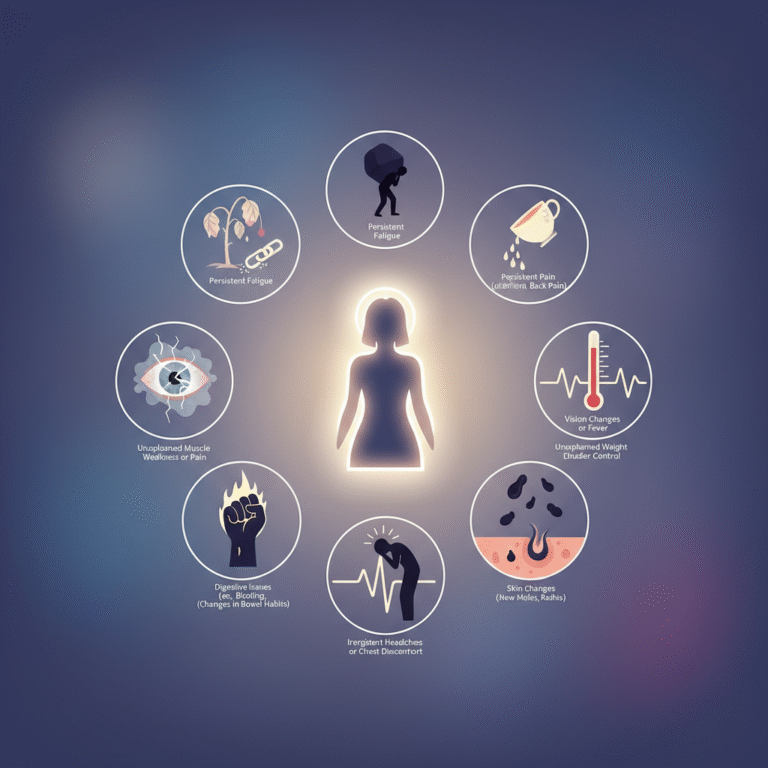
Fluid retention is one of the most common and least understood conditions affecting women of all ages. For many women, swelling becomes part of everyday life and is often dismissed as a normal reaction to heat, hormones, or long days on their feet.
Tight shoes in the evening, heavy legs without physical exertion, and deep sock marks are frequently ignored. However, when the body retains fluid regularly, it is signaling that internal systems are under strain and not functioning efficiently.
Swelling is not merely an aesthetic issue. It reflects how well the body manages circulation, hormones, and waste elimination. Learning to recognize the signs of excessive fluid retention is essential for protecting long-term health, comfort, and mobility.

What Is Fluid Retention
Fluid retention, also known as edema, occurs when excess water accumulates in the body’s tissues instead of being eliminated through the kidneys and lymphatic system. This buildup most commonly affects the feet, ankles, legs, and hands. While fluid retention can occur in anyone, women are significantly more affected due to hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause.
When the circulatory or lymphatic systems struggle to return fluid efficiently to the heart, water begins to pool in the tissues. Over time, this creates pressure beneath the skin, leading to swelling, discomfort, and a heavy sensation in the affected areas.
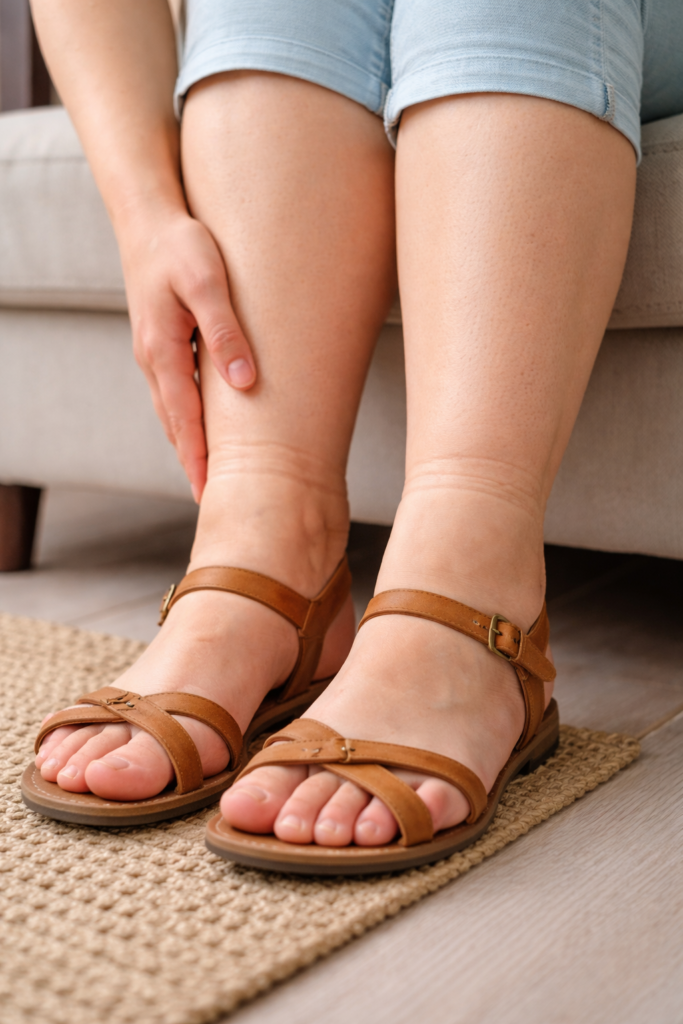
Frequent Swelling in the Feet and Ankles
One of the earliest and most obvious signs of fluid retention is swelling that appears gradually throughout the day. Many women wake up with normal-looking legs and feet, only to notice progressive swelling by late afternoon or evening. Ankles may lose their natural definition, and shoes may feel increasingly tight. This daily pattern strongly suggests difficulty in fluid drainage.
Deep Marks Left by Socks or Shoes
Persistent indentations left by socks, sandals, or tight footwear are a classic sign of fluid retention. When these marks remain visible for an extended period, it indicates that excess fluid is trapped in the tissues. The increased pressure caused by fluid accumulation makes the skin more susceptible to compression.
Heaviness and Stiffness in the Legs
A constant feeling of heaviness, tightness, or stiffness in the legs is another common symptom. Many women describe their legs as feeling tired or weighed down, even without engaging in physical activity. This sensation often worsens after prolonged sitting or standing and is directly linked to impaired circulation and fluid buildup.
Understanding how hormones influence swelling in women is essential, as hormonal shifts play a significant role in how the body manages water balance.
Rapid and Unexplained Weight Fluctuations
Sudden weight gain of one to two pounds within a short period, without changes in diet or exercise, is often due to fluid retention rather than fat accumulation. This type of weight fluctuation is especially common before menstruation but becomes concerning when it occurs frequently and unpredictably.
Changes in Skin Appearance
Excess fluid can alter the appearance of the skin. The skin may look unusually smooth, stretched, or slightly shiny, particularly around the lower legs and ankles. In some cases, pressing the skin with a finger leaves a temporary indentation, a condition known as pitting edema, which is a clear sign of fluid buildup.
Difficulty Wearing Shoes That Normally Fit
Shoes that typically fit comfortably may begin to feel tight or restrictive by the end of the day. This change is not caused by an increase in foot size but by swelling from fluid retention. Many women notice that this discomfort follows a predictable daily pattern.
Swelling That Worsens in Hot Weather
Heat causes blood vessels to expand, which can slow the return of blood and fluid to the heart. If swelling becomes significantly worse during warm weather, it suggests that the circulatory system is already under pressure and struggling to manage fluid balance effectively.
Tingling or Mild Discomfort in Swollen Areas
In some cases, fluid accumulation places pressure on nearby nerves, leading to sensations such as tingling, numbness, or mild discomfort. While these symptoms are usually not severe, they indicate that tissues are under stress due to excess fluid.
Occasional Fluid Retention Versus Chronic Fluid Retention
Occasional fluid retention is common and usually temporary. It may occur after consuming salty foods, traveling for long periods, spending extended time sitting or standing, or during hot weather. In these situations, swelling typically improves with hydration, movement, and rest.
Chronic fluid retention is characterized by frequent or daily swelling that worsens as the day progresses. It often affects comfort, mobility, and confidence. Persistent swelling may be associated with circulation issues, inflammation, or hormonal imbalance and should not be ignored.
Why Women Are More Prone to Fluid Retention
Hormonal fluctuations are a major factor. Estrogen directly influences how the body stores and releases water. During certain phases of the menstrual cycle, elevated estrogen levels promote fluid retention, leading to swelling and bloating.
The menstrual cycle itself plays a significant role, with many women experiencing noticeable swelling in the days leading up to their period. Hormonal contraceptives can further contribute, as some formulations increase water retention as a side effect.
Menopause introduces additional challenges, as hormonal changes affect circulation, metabolism, and fluid regulation. At the same time, lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior and high sodium intake can intensify fluid retention.
Prolonged sitting is particularly problematic. Limited movement reduces muscle contractions in the legs, which are essential for pushing fluid back toward the heart. Without this natural mechanism, fluid accumulates in the lower extremities.
The Impact of Fluid Retention on Quality of Life
Beyond physical discomfort, fluid retention can affect emotional well-being and daily life. Many women feel frustrated by constant swelling, struggle with clothing fit, and experience reduced confidence. Discomfort in the legs can interfere with sleep and contribute to ongoing fatigue.
When Swelling Is No Longer Normal
Occasional swelling that resolves quickly is usually harmless. However, swelling that occurs daily, worsens throughout the day, or causes persistent discomfort is a sign that the body needs attention. Identifying patterns and triggers is essential for understanding whether fluid retention has become a chronic issue.
What to Observe Moving Forward
If you recognize several of these signs, start paying close attention to your daily habits. Notice how long you remain seated, how your body responds to heat, and whether swelling improves with rest. These observations provide valuable insight into what your body may be signaling.
Discover natural solutions used by thousands of women
Fluid retention should not be ignored or accepted as an unavoidable part of life. The body communicates clearly when something is out of balance, and swelling is one of its most visible signals.
By recognizing the signs of excessive fluid retention, women can take the first step toward improving circulation, comfort, and overall well-being. Listening to these signals empowers you to seek lasting solutions rather than temporary relief.
You have not enough Humanizer words left. Upgrade your Surfer plan.